Fiber optic cable uses one or more optical fibers to transmit large amounts of information at the speed of light, which plays an important role in optic communication network. As a new generation of transmission medium, fiber optic cable has a great improvement in the quality, safety, reliability, transmission speed and transmission capacity. Besides, the transmission distance of fiber optic cable has achieved dozens of km, which is the first option to be used in large-scale network.
Fiber optic cable consists of the core, the cladding, the coating, strengthening fibers and the cable jacket (shown in the following figure.).
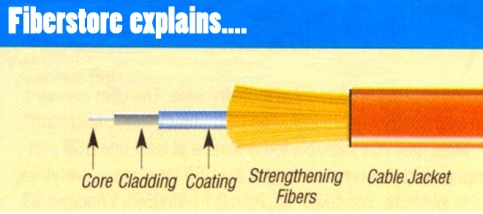
Core: The core is characterized by its diameter and it is a cylinder of glass or plastic that runs along the fiber’s length. And it is the light transmitting region of the fiber.
Cladding: It is the first layer around the core. The cladding causes light to be confined to the core of the fiber by total internal reflection at the boundary between the two.
Coating: It is the first non-optical layer around the cladding. The coating typically consists of one or more layers of a polymer that protect the silica structure against physical or environmental damage.
Strengthening Fibers: These are used to enhance the ability of cable to bear the load during the laying. Generally metallic or non-metallic fibers. The materials generally are metallic or non-metallic fibers.
Cable Jacket: This is the outer layer of any cable. The cable jacket is characterized by flame-retardant, damp-resistant, voltage-endurance and corrosion resistant and the main function of it is to protect the fiber optic cable.
Nowadays, different applications need different types of fiber optic cables which can be classified by different aspects.
Single-mode fiber cable: It allows only one mode of transmission. Because of this, the light can only be transmitted along the fiber core, completely avoiding optical dispersion and waste of energy. And single-mode fiber cable features low insertion loss and high return loss, good ability of adaptation to the environment, high data transfer rate and supporting simplex or duplex connector type. It is typically used in network connection which needs long distance transmission and high bandwidth.
Multimode fiber cable: It allows multiple modes of light transmission. Because of this, multimode fiber cable has higher “light-gathering” capacity. However, the quality of the signal is reduced over long distance for high dispersion and attenuation rate with this type of fiber. So multimode fiber cable is mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus.
Simplex Cable: It consists of a single strand of glass or plastic fiber. The data is transmitted almost in one direction, so it is applied in one-way data transfer.
Duplex Cable: It consists of two strands of glass or plastic fibers. Each fiber strand has independent coatings that are linked together by a thin layer of coating material. It is most used where separate transmit and receive signals are required, that is, one strand transmits in one direction while the other strand transmits in the opposite direction.
Single-core Fiber: It is designed to carry light only directly down the one core and it is often used in household.
Multi-core Fiber: It consists of more than one core. It’s a revolutionary new approach to engineer a fiber for high capacity applications and it is often used in the trunk.
Pipe Fiber Optic Cable: It is used in the access network or user resident network. Pipeline laying is generally in urban areas and the environment is better, so there is no special requirement for cable sheath.
Direct-buried Fiber Optic Cable: It is especially designed to be buried under the ground without any kind of extra covering, sheathing, or piping to protect it. Most direct-buried cables are built to specific tolerances to heat, moisture, conductivity, and soil acidity.
Aerial Fiber Optic Cable: It is used on a pole. Aerial fiber optic cable laying can make use of the existing pole line, saving construction cost and shortening the construction period. And it can adapt to a variety of natural environment.
Submarine Cable: It is wrapped with insulating materials, laying at the bottom of the sea, to set up a telecommunication transmission between countries.
Indoor Cable: It is used for indoor environment and mostly adopts tight set of structure. Its characteristics are soft and flame-retardant which can satisfy the need of indoor wiring.
Outdoor Cable: It is used for outdoor environment. And it can bear the climate change, prevent the infiltration of water, resist the ultraviolet radiation and resist other forces.
Accompanied by the continuous advancement of network technology, fiber optic cable constantly participates in the construction of telecommunications networks, the construction of the national information highway, Fiber To The Home (FTTH) and other occasions for large-scale use. Although fiber optic cable is still more expensive than other types of cable, it can support today’s high-speed data communications because it eliminates the problems of twisted-pair cable. Therefore, fiber optic cable is still a good choice for people.